
Selenium is a trace element for most organisms; its deficiency and excess are detrimental. Selenium beneficial effects are mainly due to the role of the 21st genetically encoded amino acid selenocysteine (Sec). In Caenorhabditis elegans, Sec is genetically incorporated into a single selenoprotein. Similar to mammals, a 20-fold excess of the optimal selenium requirement is harmful. To study the organismal response to selenium we performed a genetic screen for C. elegans mutants that are resistant to selenite. We isolated non-sense and missense egl-9/EGLN mutants that confer robust resistance to selenium. In contrast, hif- 1/HIF null mutant was highly sensitive to selenium, establishing a role for this transcription factor in the selenium response.
Methods
Toxicity Tests in Liquid Media Using the Infrared Tracking Device WMicrotracker. The readout is counts per unit of time (15 min). Experiments were performed in 96 well plates, using 80 synchronized L4 animals per well in a final volume of 100 μL. Four wells per condition per strain were assessed in each replica. Experiments were repeated at least three times. In all cases the counts per well at different times are normalized by the counts before adding the compound of interest or its vehicle (basal counts). To this basal activity is assigned an arbitrary value of one. All the assays include the wild-type strain and vehicle for each strain as controls.
Results
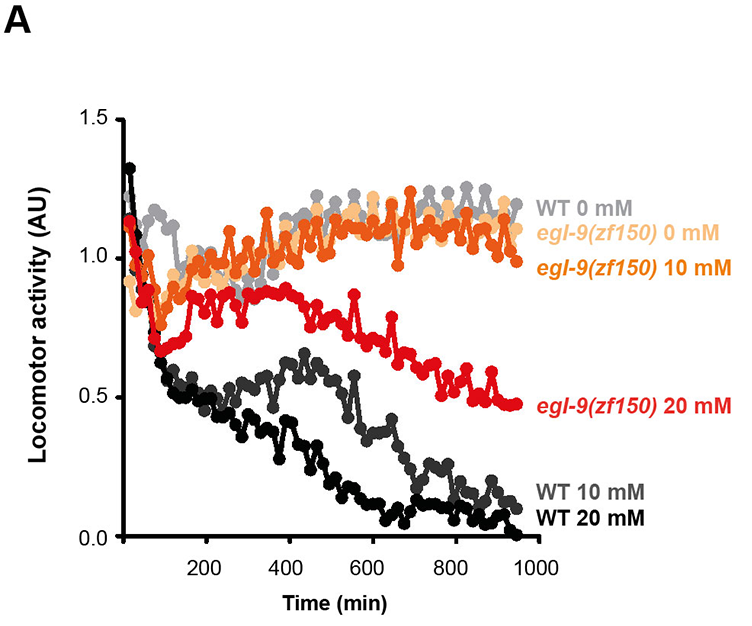
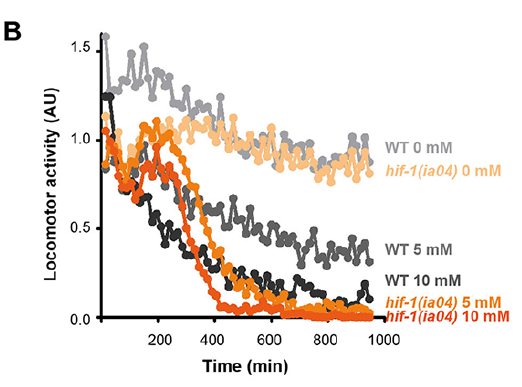
The C. elegans motility is affected with selenite in a dose-dependent manner, further phenotypic analysis was carried out using an automatic motility-based assay. Figure 2A includes typical time- and dose-dependent toxicity curves obtained using N2 and egl-9(zf150). Since EGL-9 negatively regulates HIF-1, we examined the loss-of-function hif-1(ia04) mutants for its response to selenite. This strain was more sensitive than the wild-type N2 (Figures 3B–D). In selenite conditions hif-1(ia04) mutant animals significantly decreased the locomotor activity compared to the wild-type (Figures 3B,C).
Front Genet. 2020 Feb 25;11:63. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00063.
Romanelli-Credrez L, Doitsidou M, Alkema MJ, Salinas G.
