
WMicrotracker SMART is our new technology that provides detailed information about the behavior of small animal populations, considering both time and space, including multiworm path tracking.
It is a modular system designed to quantify the behavior of small organisms in small Petri dish formats (35mm Petri dish). It enables reliable quantification of animal population movement. Additionally, it features an 8-plate carousel for automatic plate readout, programmable over time.
Main applications include C. elegans mutant characterization, animal models of diseases, and healthspan and lifespan assays in NGM.
HOW IT WORKS
The system’s functionality is based on the acquisition of a sequence of infrared imaging pictures (1 per second) and subsequent real-time processing. Depending on the configuration, it has the ability to work in two different modes:
Infrared images, plate upside down: This arrangement allows for tracking the path of multiple adult C. elegans (or worms of similar size) using NGM-type solid medium cultures. The method is based on an optical phenomenon of Silhouette Amplification by Infrared Refraction. Infrared light waves refract at the worm-agar interface, generating an amplified image that is captured by a sensitive optical/HD camera system. The digital processing of the image is carried out using software specially designed for real-time data acquisition.
Infrared microbeam grid, with the plate face-up: This mode allows for the quantification of the behavior of multiple organisms larger than 0.1 mm using solid, liquid, or air cultures. It also enables the definition of the activity area on the plate for use in chemotaxis experiments. This patented method is based on detecting movement through the scattering of light caused by a grid of infrared microbeams.
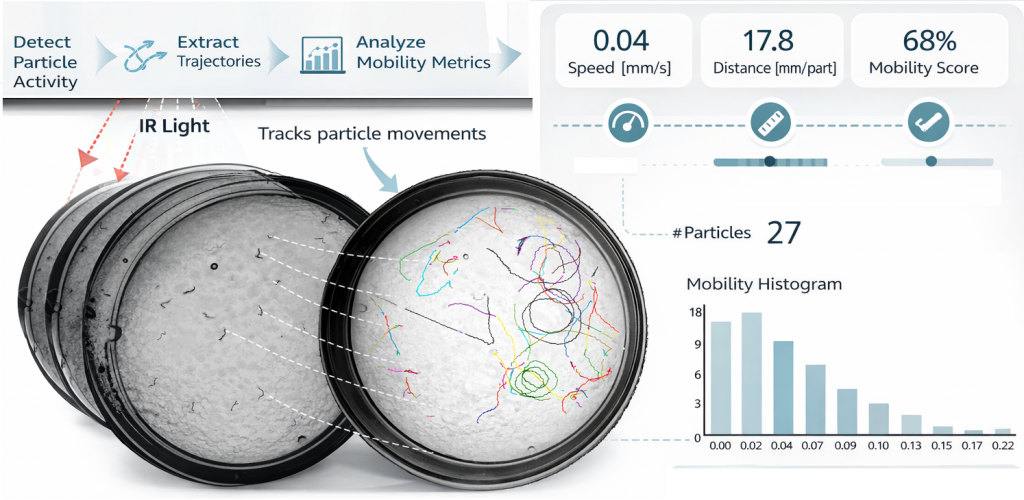
The WMicrotracker SMARTx8 uses infrared (IR) illumination and an integrated camera to continuously record the movement of small organisms within standard 35mm Petri dishes. Raw grayscale images (left) are acquired without disturbing the organisms. Detected particles are automatically tracked over time, generating individual movement trajectories (center, colored paths). From these trajectories, quantitative motility parameters are computed, including mean speed (mm/s), total distance traveled per particle (mm/particle), and a global motility score representing the fraction of actively moving organisms. Population-level results are summarized as mobility histograms and numerical indicators (right), enabling rapid, unbiased assessment of locomotor activity across experimental conditions.
![]()
FEATURES
- Simple and highly reproducible readings.
- Detection of infrared microbeam diffraction, without morphometry.
- Infrared imaging plus image processing
- Non-invasive technology: It uses very low power infrared radiation, without affecting the animals’ behaviour.
- Fast data processing: It calculates the movement in real time, with 1 to 5minutes time block resolution.
- Programmable Acquisition Cycles
![]() FOR WHOM?
FOR WHOM?
For any early stage or experienced laboratory. With affordable price for small laboratories. Focused on a varied field of experimentation. Intended for the academic and research sector, university teaching and companies.
![]() HOW DOES IT WORK?
HOW DOES IT WORK?
The system detects the movement of organism populations through infrared imaging.
Application examples
STUDIES OF DISEASE MODELS
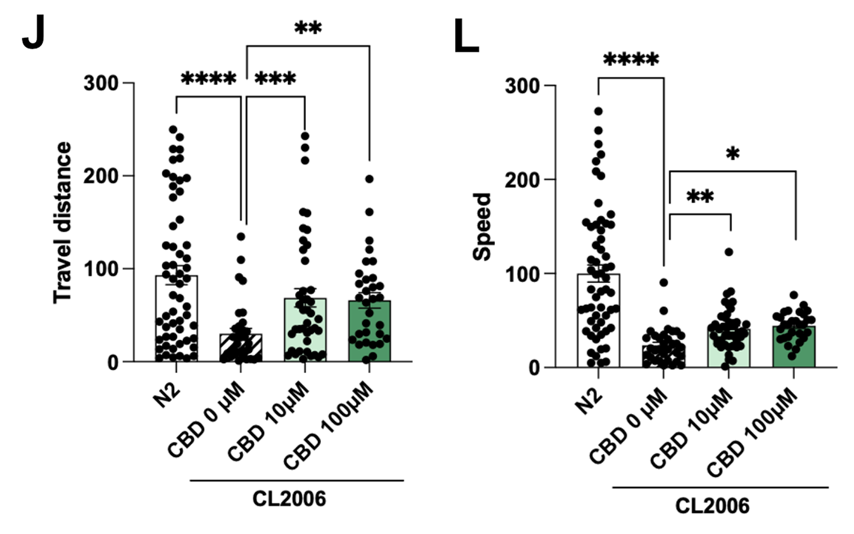
“To evaluate the impact of CBD on the progression of AD, the CL2006 strain, one of the best characterized transgenic AD strains, was employed. This strain contains the Punc-54::Aβ1–42 transgene, which results in progressive adult-onset paralysis, that has been correlated with increased levels of Aβ aggregates. As shown in Fig. 6HJ, treatment with CBD at 10 μM and 100 μM resulted in improved motility of CL2006 worms compared to the CL2006 control group. Accordingly, CBD treatment significantly increased travel distance and speed (Fig. 6JL), confirming the delay of the progressive adult-onset paralysis in CL2006.”
adapted from: “Cannabidiol as a multifaceted therapeutic agent: mitigating Alzheimer’s disease pathology and enhancing cognitive function”. Raïch et al. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy (2025) 17:10
NUTRACEUTICALS
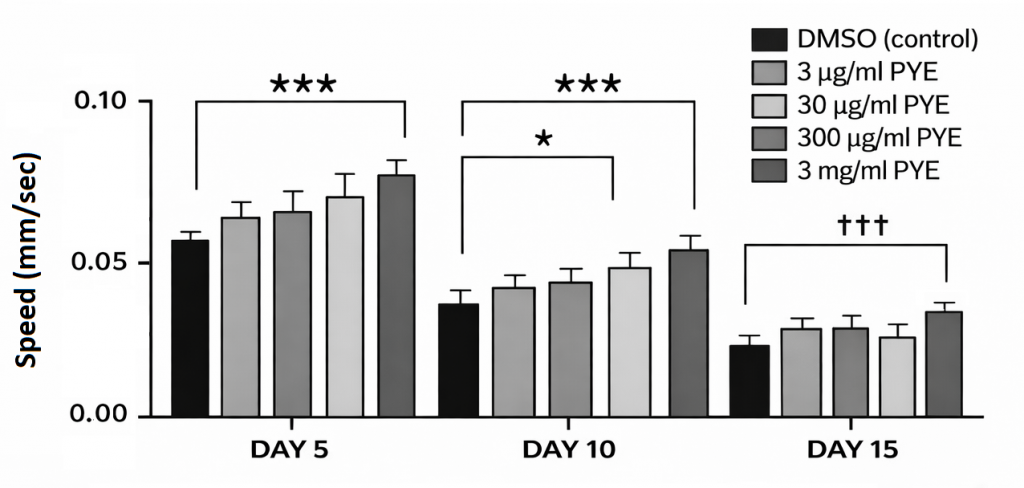
“Prunus yedoensis, known as Yoshino cherry, is common tree species in Korea. However, the fruit and its extract have not been examined for their effects on anti-aging despite its high antioxidant content including anthocyanin. Therefore, we investigated the pharmacological efficacy of P. yedoensis fruit 70% ethanol extracts (PYE) in extending lifespan and in inhibiting neurodegeneration by using Caenorhabditis elegans as a model animal. The motility in 3 mg/ml PYE treated animals were improved by 30.18, 63.33, and 58.33% at day 5, 10 and 15 respectively. Accordingly, reductions of neurodegeneration in 300 μg/ml and 3 mg/ml PYE treated animals were observed during aging.”
adapted from: “The Effects¨Prunus yedoensis Fruit Extracts on Extending Lifespan and Inhibiting Neurodegeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans” Cho YH et al.Kor J Pharmacogn 54(4):176-183(2023).
https://doi.org/10.22889/KJP.2023.54.4.176
TOXICOLOGY
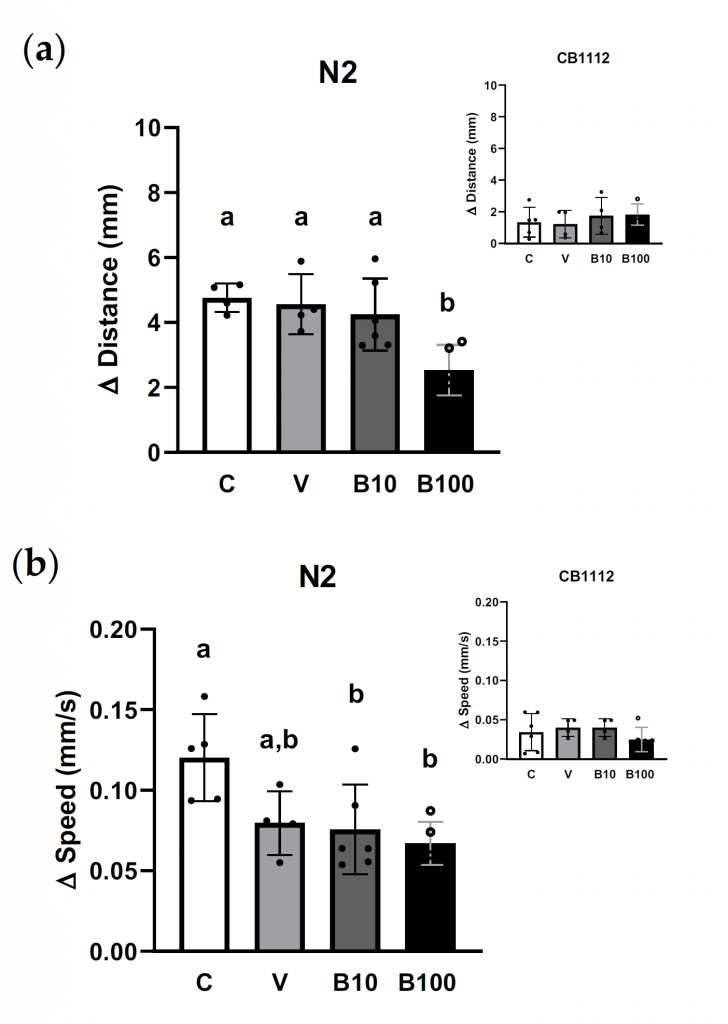
“Dithiocarbamate fungicides, including benomyl (methyl 1-butylcarbamoyl-2-benzimidazolecarbamate), share a common mechanism of toxicity by inhibiting aldehyde dehydrogenases (ALDHs), enzymes essential for detoxifying reactive aldehydes. One such aldehyde, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (DOPAL), a dopamine metabolite, is implicated in the catecholaldehyde hypothesis of Parkinson’s disease. Benomyl exposure elevated oxidative stress markers—superoxide dismutase, catalase, and lipid peroxidation—which Alda-1 reduced. Neurotoxicity was evidenced by dopaminergic dysfunction, including impaired basal slowing response, neuronal morphological abnormalities, and reduced locomotion upon optogenetic activation.
The experimental procedure was set up according to Albrecht et al. (2022) [78], adapted from Chakraborty et al., 2015 [79]. At the end of benomyl exposure, 10–15 N2 animals were transferred to plates with NGM medium. After 5 min of habituation, speed and distance traveled for 1 min were measured using WMicrotacker Smart device software (Phylumtech SA, Argentina). The results were expressed as the difference in distance traveled or speed in the absence and presence of food for both the N2 animals and the CB1112 strain, which was considered a positive control for this behavior, provided the low dopamine content resulting from the TH null mutation.”
Legend: CB1112 (cat-2(e1112) II); C = control; V = vehicle; B10 = 10 μM benomyl; B100 = 100 μM benomyl
Adpated from: “ALH Inhibition as a Molecular Initiating Event in the Adverse Outcome Pathway of Benomyl Toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans: Relevance for Parkinsonism.” Fernandez-Hubeid LE et al. Int. J.Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9163.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189163
WORM AGING ASSAY (Unpublished)
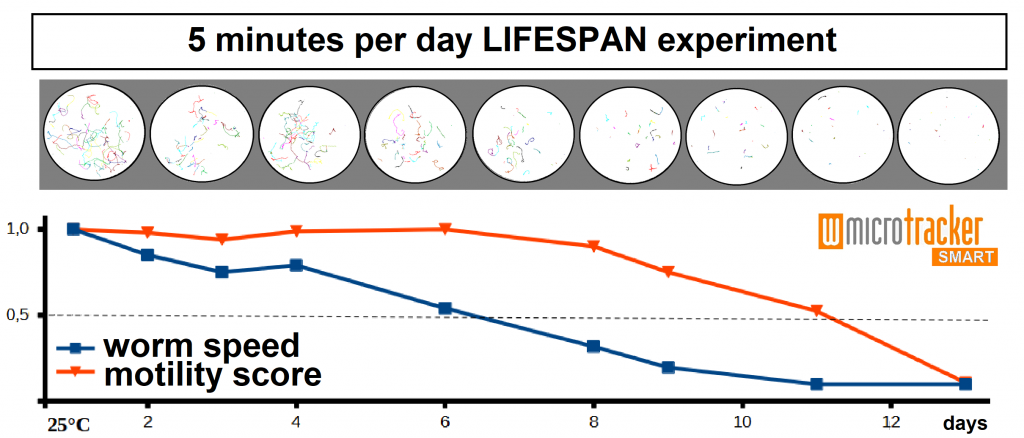
20 adult C.elegans were cultured in a 35mm Petri Dish with NGM+FuDR. Data acquisition has been performed once a day, using 5 minute acquisition lapse. Plates were subjected to “tap” stimulation before each meassure. The plot shows the single worms trails on the plate, and its reduction with age
DISTANCE VALIDATION USING IMAGEJ
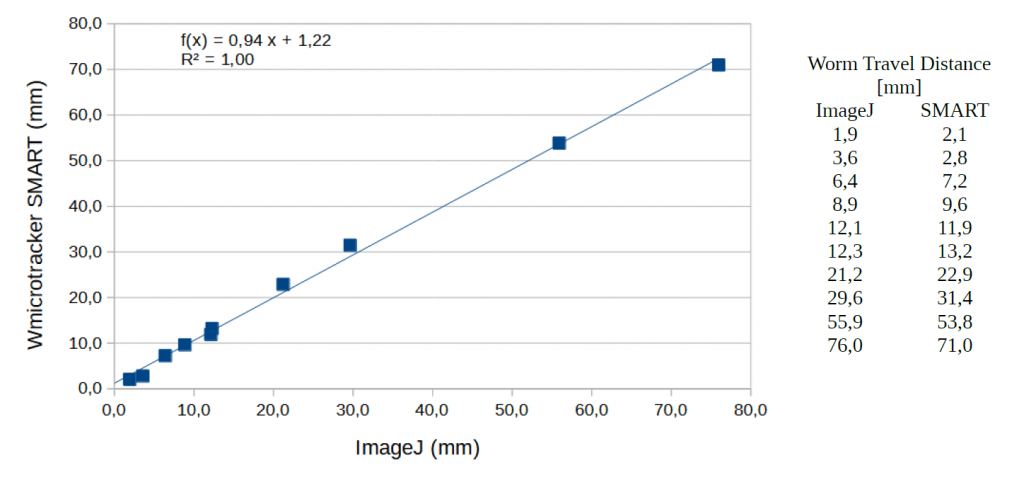
Validation of Worm distance measured with WMicrotracker SMART vs. ImageJ Manual measure
If you want to test the WMicrotracker-SMART, write us an email to info@phylumtech.com
