Application brief
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) can correct mitochondrial metabolic deficiencies related to diseases, and supraphysiological concentrations of H2S can promote good health. However, the efficacy and mechanisms of mitochondria-targeted sulfide molecules (mtH2S) administered throughout life are unknown. Using the Caenorhabditis elegans model, the effects of non-targeted H2S donors (NaGYY4137, 100 μM and 100 nM) and mtH2S (AP39, 100 nM) on lifespan and health were compared. The small doses of mtH2S required to maintain a healthy life suggest that mtH2S is a potential treatment for achieving careful aging.
Protocol
Maintenance and Experimental Design of C. elegans: For drug exposure experiments, synchronized L1 worms were cultured at 20 °C on NGM plates with E. coli OP50 containing 100 nM of AP39 + 0.01% DMSO, 100 nM or 100 mM of NaGYY4137, 0.01% DMSO, or no drug. For adult treatments, synchronized L1 larvae were cultured on NGM agar seeded only with OP50 for 60 hours until reaching young adulthood, after which drug treatments were initiated on day 0, day 2, or day 4 post-adulthood. Compound solutions were prepared fresh for each use and added to plates the night before animal transfers. Adult animals were transferred every 48 hours to fresh plates to remove progeny and maintain constant food and drug concentrations. Locomotion assays were performed using the WMicrotracker One recording system. Locomotion was measured on days 0, 2, 4, 8, 12, and 16 post-adulthood. Worms were collected from NGM plates and added to 100 μL of M9 in a flat-bottom 96-well plate. Animal movement was recorded for 30 minutes and normalized to the number of worms. Data are calculated as an average of 3 biological replicates, each with 6 technical replicates of 20 worms per well for a total of n = 120 per condition, per time point.
Results
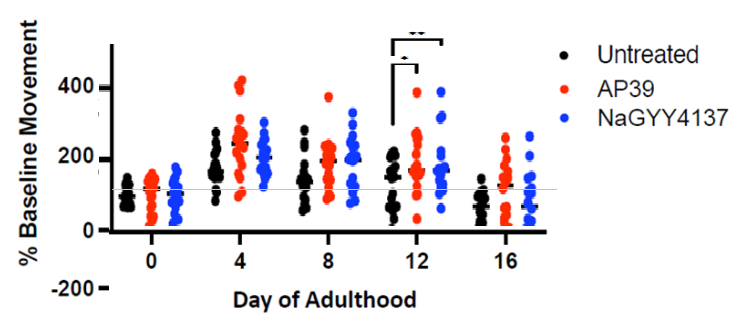
mtH2S increases lifespan and neuromuscular health of C. elegans. First, the effects of mitochondria-targeted and non-targeted H2S donors on the lifespan of C. elegans were investigated. The mitochondria-targeted sulfur supply molecule AP39 (mtH2S) significantly increased lifespan at 1000 times lower doses (100 nM) by 30% (P <0.0001), while equivalent doses of 100 nM non-targeted NaGYY4137 had no significant effect on C. elegans lifespan extension. Next, movement rates on days 0, 2, 4, 8, 12, and 16 of life were evaluated as a robust indicator of overall animal health and thus healthspan. Using wMicroTracker to measure locomotion over extended periods, the wild-type strain peaked on day 4 of adulthood (+97% compared to the initial day 0 value) and progressively decreased thereafter to a nadir of -26% on day 16 (SI Appendix, Figure S1). At very different doses, NaGYY4137 H2S 100 μM and mtH2S 100 nM increased total movement rates of animals throughout the lifespan (P <0.001), using the area under the movement curve analysis over days (Fig. 2A). In contrast, healthspan significantly increased with mtH2S when administered from day 0, 2, or 4 of adulthood (P < 0.01) and also increased with non-targeted H2S treatments from days 2 or 4 after adulthood (P < 0.05), but not on day 0 of young adulthood (Fig. 4 and SI Appendix, Figure S7).
Reference: Mitochondrial sulfide promotes life span and health span through distinct mechanisms in developing versus adult treated Caenorhabditis elegans. Vintila et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Aug 8;120(32):e2216141120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2216141120.
Keywords: Lifespan, healthspan, WMicrotracker ONE
