
The researcher group working at an FDA laboratory in the USA has adapted the WMicrotracker methodology to develop a sophisticated method for analyzing the time course of C. elegans activity. The 16-hour Worm Adult Activity Test (wAAT) can be employed to measure worm activity levels, allowing for efficient screening of pharmacological and toxicity-induced effects.
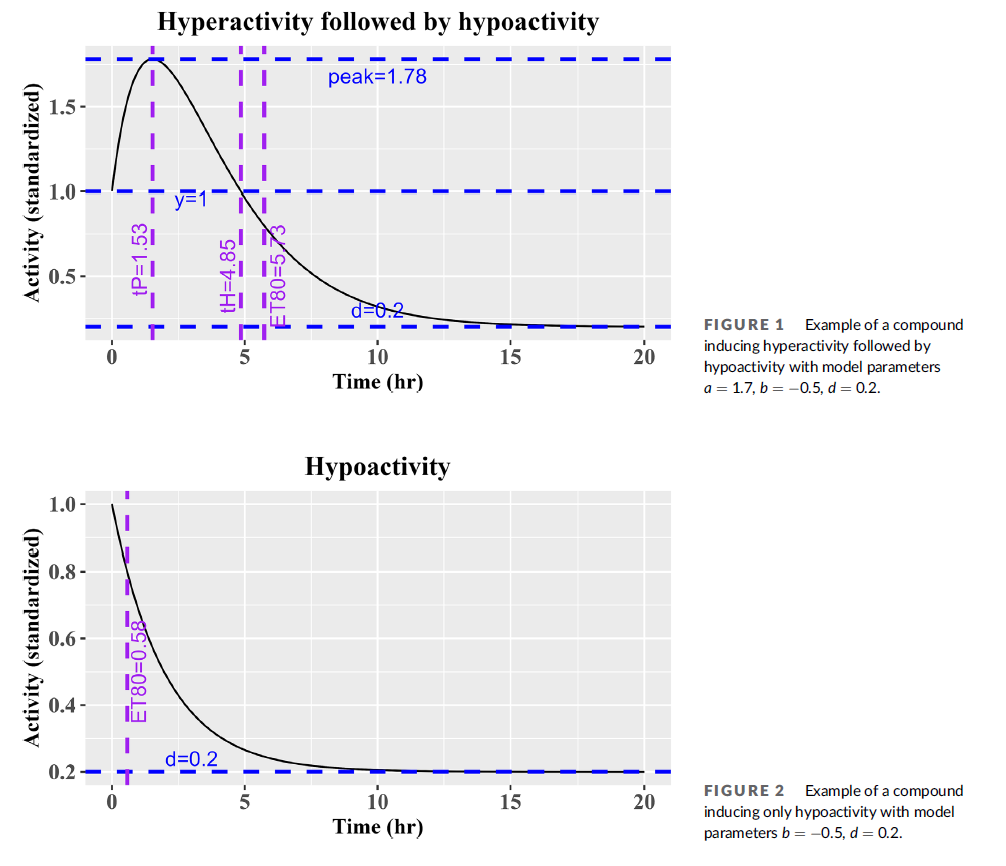
Within the manuscript, the authors describe the mathematical model used for calculations and the validation of a set of toxicants.
J Appl Toxicol. 2023 Aug 8. doi: 10.1002/jat.4525.
The worm Adult Activity Test (wAAT): A de novo mathematical model for detecting acute chemical effects in Caenorhabditis elegans
Piper Reid Hunt, Bonnie Welch, Jessica Camacho, Priyanka N. Bushana, Hugh Rand, Robert L. Sprando, Martine Ferguson.
Abstract
We have adapted a semiautomated method for tracking Caenorhabditis elegans spontaneous locomotor activity into a quantifiable assay by developing a sophisticated method for analyzing the time course of measured activity. The 16-h worm Adult Activity Test (wAAT) can be used to measure C. elegans activity levels for efficient screening for pharmacological and toxicity-induced effects. As with any apical endpoint assay, the wAAT is mode of action agnostic, allowing for detection of effects from a broad spectrum of response pathways. With caffeine as a model mild stimulant, the wAAT showed transient hyperactivity followed by reversion to baseline. Mercury chloride (HgCl2 ) produced an early dose-response hyperactivity phase followed by pronounced hypoactivity, a behavior pattern we have termed a toxicant “escape response.” Methylmercury chloride (meHgCl) produced a similar pattern to HgCl2 , but at much lower concentrations, a weaker hyperactivity response, and more pronounced hypoactivity. Sodium arsenite (NaAsO2 ) and dimethylarsinic acid (DMA) induced hypoactivity at high concentrations. Acute toxicity, as measured by hypoactivity in C. elegans adults, was ranked: meHgCl > HgCl2 > NaAsO2 = DMA. Caffeine was not toxic with the wAAT at tested concentrations. Methods for conducting the wAAT are described, along with instructions for preparing C. elegans Habitation Medium, a liquid nutrient medium that allows for developmental timing equivalent to that found with C. elegans grown on agar with OP50 Escherichia coli feeder cultures. A de novo mathematical parametric model for adult C. elegans activity and the application of this model in ranking exposure toxicity are presented.
link: https://analyticalsciencejournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jat.4525
